There are a lot of confusing terms in the computer world. RAM (Random Access Memory) is no exception to this rule. This article will introduce you to the concept of Memory Rank and their definitions.
What Is The Memory Rank?
In your computer RAM is one of the key components that contribute to the overall performance of your system. RAM is a component where applications can temporarily store data, and your CPU (Central Processing Unit) can access that data on a short-term basis.
Data access (read/write) on RAM will be handled by the memory controller, which is located on the CPU. The Memory Bus, which is a set of wires on the motherboard, shall be used for communication between the CPU and RAM. Here we take a closer look at data connections (Data Bus).
The Data Bus is 64-bit wide. While, memory chips are typically 4-bit or 8-bit wide. To maintain transmission performance, multiple memory chips must be grouped together to achieve a 64-bit wide overall. This memory group of 64-bit wide is called the memory rank.
RAM with only one memory group 64-bit is known as single-rank, two groups 64-bit make up a dual-rank or quad-rank with four groups of 64-bit.
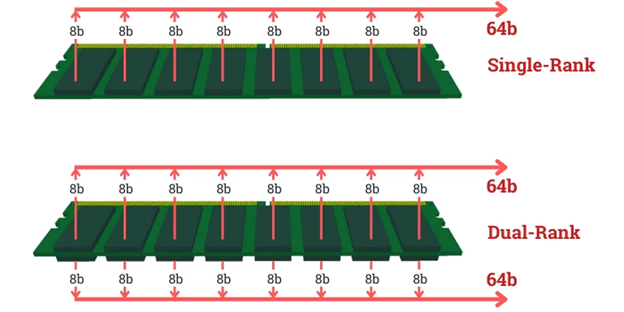
Memory Rank: Single-Rank vs Dual-Rank
Single-Rank vs Dual-Rank
On the RAM module, the memory chips can be placed on one side (single-sided) or two sides (double-sided). Single-sided RAM is typically found in low capacity modules. While higher capacity modules are usually double-sided. We will have the following types of RAM:
- Single-sided module, single-rank (only one rank);
- Double-sided module, single-rank;
- Double-sided module, dual-rank (with 2 ranks);
- Double-sided module, quad-rank (4 ranks available).
There will be questions raised, that our data bus is only 64-bit wide. Dual-rank (or multi-rank) is made up of two groups (or more) of 64-bit memory. How is transmission performed, and what is the purpose of dual-rank?
RAM is made up of a 2-dimensional matrix of memory cells. Each cell is a capacitor that stores one bit of data. These cells must be recharged frequently because they leak over time, resulting in data loss.
With the dual-rank module, the ranks will work alternately. When this rank is recharged, the other rank performs transmission with CPU (read/write). This will make dual-rank module will have higher performance than single-rank. As testing, in the same frequency and bandwidth, dual-rank will be 4 to 7 percent faster than single-rank.
Memory Rank vs Memory Channel
Each 64-bit data bus makes up a channel. The system can have one channel (single-channel), 2 channels (dual-channel), 3 channels (triple-channel), or 4 channels (quad-channel), etc. Most motherboards today support dual-channel. Some configurations for enthusiasts can support quad-channel.
When running in dual-channel mode, you must use at least two RAM modules with identical parameters (brand, capacity, speed, latency, etc.).
In some cases, mixing modules with different parameters for dual-channel mode can be used, but it is not recommended (see more in: Can you mix RAM brands).
In fact, using dual-channel increases system performance by 16-17%. Combining dual-rank and dual-channel will be a good choice for computers that typically require heavy workloads such as gaming or 3D graphics.
Conclusion
As analyzed, the performance improvement of dual-rank over single-rank is not significant. However, when combined with a dual-channel configuration or on systems with a more powerful configuration (quad-channel), this can be an interesting choice for enthusiasts looking for the pinnacle of technology.
The decision is entirely yours, and we hope this article has provided you with some useful information to assist you in upgrading or building your own PC.




